Séance du 23 janvier
This commit is contained in:
parent
f265da0cb3
commit
37755824ea
16 changed files with 232 additions and 17 deletions
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,12 @@
|
|||
\newlabel{eq:condArete}{{1}{3}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {paragraph}{preuve :}{3}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {section}{\numberline {2}Mise en pratique : graphe de Gabriel et de voisinage relatif}{3}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {section}{\numberline {3}Triangulation de Delaunay}{4}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.1}Pratique}{4}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.2}Aspect théorique}{4}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {part}{III\hspace {1em}Algorithme de Dijkstra pour la recherche du plus court chemin}{4}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {2.1}Création de graphe de Gabriel et de voisinage relatif}{3}}
|
||||
\@writefile{lof}{\contentsline {figure}{\numberline {2}{\ignorespaces Graphe de gabriel\relax }}{4}}
|
||||
\newlabel{fig:2_4_gabriel}{{2}{4}}
|
||||
\@writefile{lof}{\contentsline {figure}{\numberline {3}{\ignorespaces Graphe de voisinage realtif\relax }}{5}}
|
||||
\newlabel{fig:2_4_gvr}{{3}{5}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {section}{\numberline {3}Triangulation de Delaunay}{6}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.1}Pratique}{6}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.2}Aspect théorique}{6}}
|
||||
\@writefile{toc}{\contentsline {part}{III\hspace {1em}Algorithme de Dijkstra pour la recherche du plus court chemin}{6}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,2 +1,4 @@
|
|||
\select@language {french}
|
||||
\contentsline {figure}{\numberline {1}{\ignorespaces Différentes positions possible de points par rapport à $A$ et $B$\relax }}{3}
|
||||
\contentsline {figure}{\numberline {2}{\ignorespaces Graphe de gabriel\relax }}{4}
|
||||
\contentsline {figure}{\numberline {3}{\ignorespaces Graphe de voisinage realtif\relax }}{5}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
|
|
@ -64,7 +64,35 @@ Réciproquement, si tous les points de $\mathcal{V}$ sont à l'extérieur du cer
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
\section{Mise en pratique : graphe de Gabriel et de voisinage relatif}
|
||||
Questions 2.4 2.5 2.6
|
||||
\subsection{Création de graphe de Gabriel et de voisinage relatif}
|
||||
\begin{figure}
|
||||
\centering
|
||||
\includegraphics[width=1\linewidth]{images/2_4_gabriel}
|
||||
\caption{Graphe de gabriel}
|
||||
\label{fig:2_4_gabriel}
|
||||
\end{figure}
|
||||
\begin{figure}
|
||||
\centering
|
||||
\includegraphics[width=1\linewidth]{images/2_4_gvr}
|
||||
\caption{Graphe de voisinage realtif}
|
||||
\label{fig:2_4_gvr}
|
||||
\end{figure}
|
||||
|
||||
En traçant les graphes de Gabriel (figure \ref{fig:2_4_gabriel}) et de voisinage relatif (figure \ref{fig:2_4_gvr}), on observe que le second est inclus dans le premier.
|
||||
|
||||
\subsection{Génération d'un réseau}
|
||||
En combinant la génération de graphe de Gabriel et de voisinage relatif, on peut générer un réseau routier, comme le montre la figure \ref{fig:2_5}.
|
||||
|
||||
\begin{figure}
|
||||
\centering
|
||||
\includegraphics[width=1\linewidth]{images/2_5}
|
||||
\caption{Réseau généré}
|
||||
\label{fig:2_5}
|
||||
\end{figure}
|
||||
|
||||
\subsection{Temps de génération d'un réseau}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
\section{Triangulation de Delaunay}
|
||||
\subsection{Pratique}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,8 @@
|
|||
\contentsline {section}{\numberline {1}Condition pour un graphe de Gabriel}{3}
|
||||
\contentsline {paragraph}{preuve :}{3}
|
||||
\contentsline {section}{\numberline {2}Mise en pratique : graphe de Gabriel et de voisinage relatif}{3}
|
||||
\contentsline {section}{\numberline {3}Triangulation de Delaunay}{4}
|
||||
\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.1}Pratique}{4}
|
||||
\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.2}Aspect théorique}{4}
|
||||
\contentsline {part}{III\hspace {1em}Algorithme de Dijkstra pour la recherche du plus court chemin}{4}
|
||||
\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {2.1}Création de graphe de Gabriel et de voisinage relatif}{3}
|
||||
\contentsline {section}{\numberline {3}Triangulation de Delaunay}{6}
|
||||
\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.1}Pratique}{6}
|
||||
\contentsline {subsection}{\numberline {3.2}Aspect théorique}{6}
|
||||
\contentsline {part}{III\hspace {1em}Algorithme de Dijkstra pour la recherche du plus court chemin}{6}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
BIN
compte_rendu/images/2_5.png
Normal file
BIN
compte_rendu/images/2_5.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 
(image error) Size: 35 KiB |
BIN
compte_rendu/images/2_6_lin.png
Normal file
BIN
compte_rendu/images/2_6_lin.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 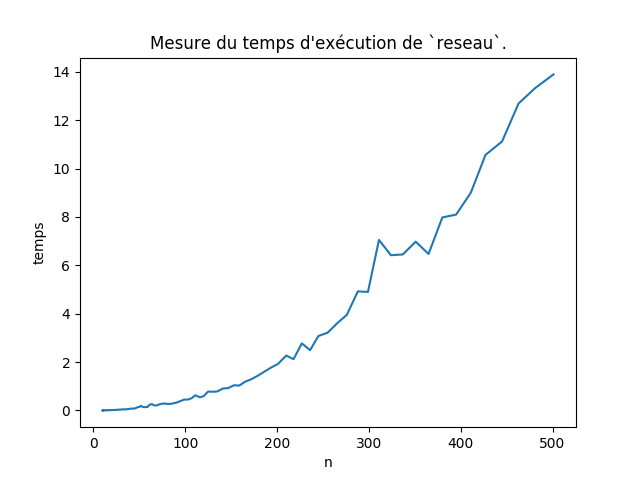
(image error) Size: 23 KiB |
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_6.png
Normal file
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_6.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 
(image error) Size: 38 KiB |
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_7_cout.png
Normal file
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_7_cout.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 
(image error) Size: 18 KiB |
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_7_graphe.png
Normal file
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_7_graphe.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 
(image error) Size: 40 KiB |
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_8_simple.png
Normal file
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_8_simple.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 
(image error) Size: 41 KiB |
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_9.png
Normal file
BIN
compte_rendu/images/4_9.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 
(image error) Size: 30 KiB |
91
graphe.py
91
graphe.py
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,7 @@ import numpy as np
|
|||
|
||||
import triangulation
|
||||
import tas
|
||||
import stack
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Graphe:
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,7 +22,7 @@ class Graphe:
|
|||
self.nom = nom
|
||||
self.sommets = []
|
||||
self.aretes = []
|
||||
self.cout = None, Graphe.Cout.TEMPS
|
||||
self.cout = Graphe.Cout.TEMPS
|
||||
self.arrivee = None
|
||||
|
||||
def renomme(self, nom):
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,6 +56,8 @@ class Graphe:
|
|||
"""
|
||||
a = Arete(s1, s2, longueur, v_moyenne, self)
|
||||
self.aretes.append(a)
|
||||
s1.aretes.add(a)
|
||||
s2.aretes.add(a)
|
||||
return a
|
||||
|
||||
def n(self):
|
||||
|
|
@ -303,18 +306,19 @@ class Graphe:
|
|||
minCout = sys.float_info.max
|
||||
matrice = self.matriceCout(tournee)
|
||||
cout = 0
|
||||
visite = [False]*len(tournee)
|
||||
visite = [False] * len(tournee)
|
||||
visite[0] = True
|
||||
itineraire = [0]
|
||||
|
||||
def backtrack():
|
||||
nonlocal meilleurItineraire, minCout, matrice, cout, visite, itineraire
|
||||
if cout < minCout:
|
||||
if len(itineraire)==len(tournee):
|
||||
if len(itineraire) == len(tournee):
|
||||
if cout + matrice[0, itineraire[-1]] < minCout:
|
||||
minCout = cout + matrice[0, itineraire[-1]]
|
||||
meilleurItineraire = [tournee[x] for x in itineraire]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for i,sommet_visite in enumerate(visite):
|
||||
for i, sommet_visite in enumerate(visite):
|
||||
if not sommet_visite:
|
||||
visite[i] = True
|
||||
indicePrec = itineraire[-1]
|
||||
|
|
@ -328,12 +332,82 @@ class Graphe:
|
|||
return minCout, meilleurItineraire
|
||||
|
||||
def traceItineraire(self, itineraire):
|
||||
for i,x in enumerate(itineraire):
|
||||
for i, x in enumerate(itineraire):
|
||||
x.nom = "s" + str(i)
|
||||
suivant = itineraire[(i+1)%len(itineraire)]
|
||||
c,_ = self.astar(x, suivant)
|
||||
suivant = itineraire[(i + 1) % len(itineraire)]
|
||||
c, _ = self.astar(x, suivant)
|
||||
self.colorieChemin(c, (0.8, 0.1, 0.8))
|
||||
|
||||
def Prim(self):
|
||||
for s in self.sommets:
|
||||
s.selection = False
|
||||
for a in self.aretes:
|
||||
a.selection = False
|
||||
aretes = tas.Tas(lambda x: -x.cout)
|
||||
for a in self.sommets[0].aretes:
|
||||
aretes.ajoute(a)
|
||||
self.sommets[0].selection = True
|
||||
arbre = []
|
||||
ptot = 0
|
||||
while not aretes.empty():
|
||||
a = aretes.pop()
|
||||
s1, s2 = a.s1, a.s2
|
||||
if not s1.selection or not s2.selection:
|
||||
a.selection = True
|
||||
ptot += a.cout
|
||||
if not s1.selection:
|
||||
s1.selection = True
|
||||
for a_1 in s1.aretes:
|
||||
aretes.ajoute(a_1)
|
||||
if not s2.selection:
|
||||
s2.selection = True
|
||||
for a_2 in s2.aretes:
|
||||
aretes.ajoute(a_2)
|
||||
return ptot
|
||||
|
||||
def colorieSelection(self, couleur=(0.1, 0.6, 0.2)):
|
||||
"""Colorie les sommets et arêtes avec le drapeau `selection` à True."""
|
||||
for s in self.sommets:
|
||||
if s.selection:
|
||||
s.couleur = couleur
|
||||
for s in self.aretes:
|
||||
if s.selection:
|
||||
s.couleur = couleur
|
||||
|
||||
def grapheDeCout(self, tournee):
|
||||
g = Graphe("Graphe de cout de " + self.nom)
|
||||
for s in tournee:
|
||||
s_a = g.ajouteSommet(s.x(), s.y())
|
||||
s_a.image = s
|
||||
s.image = s_a
|
||||
|
||||
for i, s in enumerate(g.sommets):
|
||||
self.dijkstraAvecTas(s.image)
|
||||
for s_v in g.sommets[i:]:
|
||||
d = sum((a.cout for a in self.cheminOptimal(s_v.image)))
|
||||
g.connecte(s, s_v, d, 1)
|
||||
return g
|
||||
|
||||
def tourneeApproximative(self, tournee):
|
||||
g_cout = self.grapheDeCout(tournee)
|
||||
g_cout.Prim()
|
||||
pile = stack.Stack()
|
||||
pile.add(tournee[0].image)
|
||||
tournee[0].image.selection = False
|
||||
chemin = [tournee[0]]
|
||||
while not pile.empty():
|
||||
actuel = pile.pop()
|
||||
fils = list(filter(lambda x: x.selection, actuel.aretes))
|
||||
if fils:
|
||||
a = fils.pop()
|
||||
a.selection = False
|
||||
nouveau = a.voisin(actuel)
|
||||
nouveau.selection = False
|
||||
chemin.append(nouveau.image)
|
||||
pile.add(actuel)
|
||||
pile.add(nouveau)
|
||||
return chemin
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Sommet:
|
||||
"""Implémente un sommet de graphe."""
|
||||
|
|
@ -352,6 +426,8 @@ class Sommet:
|
|||
self.cumul = None
|
||||
self.precedent = None
|
||||
self.graphe = graphe
|
||||
self.selection = False
|
||||
self.image = None
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def minCumulRestant(self):
|
||||
|
|
@ -409,6 +485,7 @@ class Arete:
|
|||
self.v_moyenne = v_moyenne
|
||||
self.couleur = couleur
|
||||
self.graph = graph
|
||||
self.selection = False
|
||||
|
||||
def voisin(self, s):
|
||||
"""Retourne le sommet voisin de s dans l'arête.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
22
stack.py
Normal file
22
stack.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
|||
class Stack:
|
||||
class StackElem:
|
||||
def __init__(self, elt, prec):
|
||||
self.elt = elt
|
||||
self.prec = prec
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, elts=[]):
|
||||
self.first = None
|
||||
for e in elts:
|
||||
self.add(e)
|
||||
|
||||
def add(self, e):
|
||||
se = self.StackElem(e, self.first)
|
||||
self.first = se
|
||||
|
||||
def pop(self):
|
||||
e = self.first.elt
|
||||
self.first = self.first.prec
|
||||
return e
|
||||
|
||||
def empty(self):
|
||||
return self.first is None
|
||||
82
test.py
82
test.py
|
|
@ -6,6 +6,7 @@ Donc pour la question 3_4 : `python3 test.py 3_4`.
|
|||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
import graphe
|
||||
import graphique
|
||||
|
|
@ -101,7 +102,7 @@ def chronometre(fonctionTest, fonctionPreparation, parametres):
|
|||
def testQuestion2_6():
|
||||
"""Mesure la performance de graphe.reseau"""
|
||||
prepare = lambda p : graphe.pointsAleatoires(p, 10)
|
||||
valeurs_n = np.arange(1, 200)
|
||||
valeurs_n = list(map(int, np.logspace(1, 2.7, 100)))
|
||||
temps = chronometre(graphe.reseau, prepare, valeurs_n)
|
||||
pl.close('all')
|
||||
pl.title("Mesure du temps d'exécution de `reseau`.")
|
||||
|
|
@ -347,6 +348,85 @@ def testQuestion4_2():
|
|||
graphique.affiche(g, (0, 0), 10.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def testQuestion4_3():
|
||||
"""Mesure le temps de calcul."""
|
||||
g = graphe.reseauRapide(graphe.pointsAleatoires(1000, 1000))
|
||||
prepare = lambda p : random.sample(g.sommets, p)
|
||||
valeurs_n = list(map(int, np.linspace(1, 15, 10)))
|
||||
temps = chronometre(g.voyageurDeCommerceNaif, prepare, valeurs_n)
|
||||
pl.close('all')
|
||||
pl.title("Temps d'exécution pour le voyageur de commerce.")
|
||||
pl.plot(valeurs_n, temps)
|
||||
pl.xlabel("n (nombre de points de la tournée)")
|
||||
pl.ylabel("temps")
|
||||
pl.show()
|
||||
pl.title("Temps d'exécution pour le voyageur de commerce.")
|
||||
pl.loglog(valeurs_n, temps)
|
||||
pl.xlabel("n (nombre de points de la tournée)")
|
||||
pl.ylabel("temps")
|
||||
pl.show()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def testQuestion4_6():
|
||||
g = graphe.pointsAleatoires(30, 30)
|
||||
|
||||
graphe.reseauRapide(g)
|
||||
g.fixeTempsCommeCout()
|
||||
g.renomme("Algorithme de Prim (cout=temps)")
|
||||
p = g.Prim()
|
||||
print("Poids de prim:", p)
|
||||
g.colorieSelection()
|
||||
graphique.affiche(g, (0, 0), 10.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def testQuestion4_7():
|
||||
g = graphe.pointsAleatoires(30, 30)
|
||||
|
||||
graphe.reseauRapide(g)
|
||||
g.fixeTempsCommeCout()
|
||||
g.renomme("Graphe de test (cout=temps)")
|
||||
tournee = [g.sommets[i] for i in (0, 1, 2, 7)]
|
||||
g1 = g.grapheDeCout(tournee)
|
||||
graphique.affiche(g, (0, 0), 10., blocage=False)
|
||||
graphique.affiche(g1, (0, 0), 10.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def testQuestion4_8():
|
||||
g = graphe.pointsAleatoires(30, 30)
|
||||
|
||||
graphe.reseauRapide(g)
|
||||
g.fixeTempsCommeCout()
|
||||
g.renomme("Graphe de test (cout=temps)")
|
||||
g1 = copy.deepcopy(g)
|
||||
print("Tournée 0, 1, 2, 7")
|
||||
tournee = [g.sommets[i] for i in (0, 1, 2, 7)]
|
||||
iti = g.tourneeApproximative(tournee)
|
||||
g.traceItineraire(iti)
|
||||
tournee = [g1.sommets[i] for i in (0, 1, 2, 7)]
|
||||
cout,iti = g1.voyageurDeCommerceNaif(tournee)
|
||||
g1.traceItineraire(iti)
|
||||
graphique.affiche(g, (0, 0), 10., blocage=False)
|
||||
graphique.affiche(g1, (0, 0), 10.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def testQuestion4_9():
|
||||
"""Mesure le temps de calcul."""
|
||||
g = graphe.reseauRapide(graphe.pointsAleatoires(1000, 1000))
|
||||
prepare = lambda p : random.sample(g.sommets, p)
|
||||
valeurs_n = list(map(int, np.logspace(1, 2, 30)))
|
||||
temps = chronometre(g.tourneeApproximative, prepare, valeurs_n)
|
||||
pl.close('all')
|
||||
pl.title("Temps d'exécution pour le voyageur de commerce approximatif.")
|
||||
pl.plot(valeurs_n, temps)
|
||||
pl.xlabel("n (nombre de points de la tournée)")
|
||||
pl.ylabel("temps")
|
||||
pl.show()
|
||||
pl.title("Temps d'exécution pour le voyageur de commerce approximatif.")
|
||||
pl.loglog(valeurs_n, temps)
|
||||
pl.xlabel("n (nombre de points de la tournée)")
|
||||
pl.ylabel("temps")
|
||||
pl.show()
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
n = sys.argv[1]
|
||||
if n in ('--help', '-h'):
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Reference in a new issue